Graphene Oxide, 2–5 Layer | Surface Area: 420 m²/g
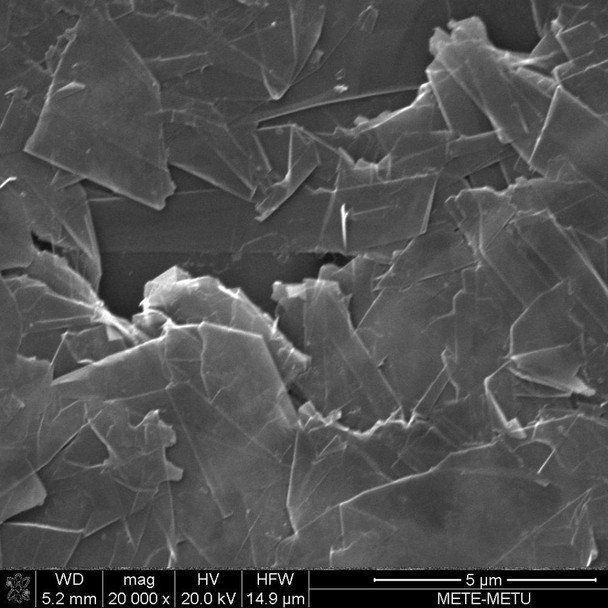
Graphene Oxide (GO) is produced by oxidizing graphite using strong oxidizing agents, resulting in a material composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen in varying ratios. While its structure and properties depend on the synthesis method and degree of oxidation, GO retains the layered structure of the original graphite.
One of the key advantages of Graphene Oxide over other 2D materials—such as pristine graphene—is its excellent dispersibility in solution, even at high concentrations. This characteristic makes GO especially suitable for applications such as optical coatings, transparent conductors, thin-film batteries, chemical-resistant coatings, water purification, and more.
At Nanografi, we supply high-quality Graphene Oxide to meet the diverse needs of our customers.
Technical Properties of Graphene Oxide
Purity: 99.8%
Average Number of Layers: Few-Layer Graphene Oxide
Average Diameter (µm): 4.5
Surface Area (m²/g): ≥ 420
Carbon Content (%C): 60–80
Oxygen Content (%O): 10–30
Hydrogen Content (%H): ≤ 2.00
Nitrogen Content (%N): ≤ 0.50
Color: Dark Brown
Particle Size (µm): 5–40
Applications of Graphene Oxide
- Composite materials
- Thermal management and heat spreading
- Graphene-polymer composites
- Graphene Oxide paper
- Transparent and conductive GO coatings
- Solar cells
- Supercapacitors (GO-based)
- Low-permeability materials
- High-barrier packaging
- Electro-static dissipation (ESD) films
- Support material for metallic catalysts
- Chemical and biological GO sensors
- Multifunctional graphene-based materials
- Graphene research